Recently, a new report from Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) shows that the deployment of floating PV system in Asia is developing rapidly. Then, this means that the need of floating solar racking is increasing accordingly. Sara Jane Ahmed and elrika Hamdi, IEEFA analysts, pointed out that electricity demand in the Philippines and Malaysia fell as much as 16% during the covid-19 lock-in period. Although Vietnam and Singapore, the two countries with less stringent control measures and less power demand decline, are still causing great pressure on the power grid.
"If the covid-19 epidemic could teach us a lesson, it's that utility companies needing to be flexible in their operations, instead of outdated power stations that burn coal 24 hours a day and can't respond quickly to sudden changes or blackouts," said elrika Hamdi. Our research shows that more and more ASEAN countries are building solar power plants floating on rivers, dams, lakes and reservoirs (even oceans) to produce clean electricity at a price that can compete with electricity from polluting coal-fired power plants. " Solar farms are best located near hydroelectric facilities and can carry existing grid connections, the report said. Floating solar energy can also balance the peaks and troughs of consumer demand in complex power systems.
"A combination of floating solar and hydroelectric power on existing dams and reservoirs is more economical than coal-fired power plants that add new base loads to the grid system," said Sara Jane Ahmed, "It can withstand typhoons, strong waves and strong winds with the speed up to 170 km / h, and the manufacturers are currently testing offshore FPVs.

The first FPV system was built in Aichi Prefecture of Japan in 2007, and China is the largest FPV manufacturer. Till the end of 2018, the total installed capacity of FPV in Japan and China is 1.3GW, while Vietnam has installed 47MW FPV. Recently, India's largest power generation company (NTPC) has confirmed that it is developing 200 MW FPV in four locations, making it as one of the largest developers in the world.
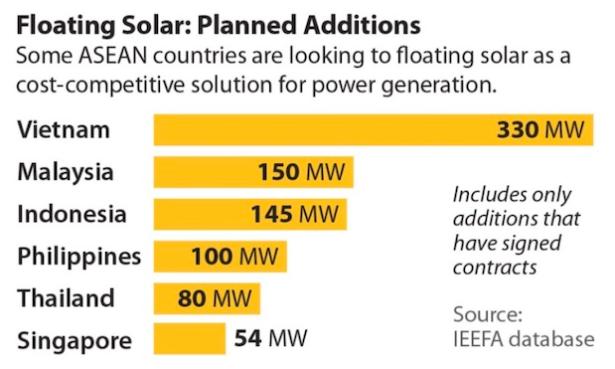
At present, some ASEAN countries are using floating solar energy as a solution for power generation cost competition. There is at least five countries having announced the large-scale floating solar energy plans (as shown in the figure below).